Quality Improvement (QI) involves a systematic and coordinated approach to solving a problem using specific methods and tools with the aim of bringing about a measurable improvement.
QI is the process of engaging appropriate methodologies and quality management tools to close the gap between current and desired levels of performance 1. There are a variety of methods to improve quality of care which are already accepted and used in maternal and newborn health. These include: conducting maternal and perinatal death audit or review, ‘near-miss’ audit and standards-based audit.
All three types of audit essentially ask the questions: What was done well and what could have been done differently to avoid maternal or perinatal death. Where audit system is implemented, it helps identify which areas of clinical care or the health systems require improvement.
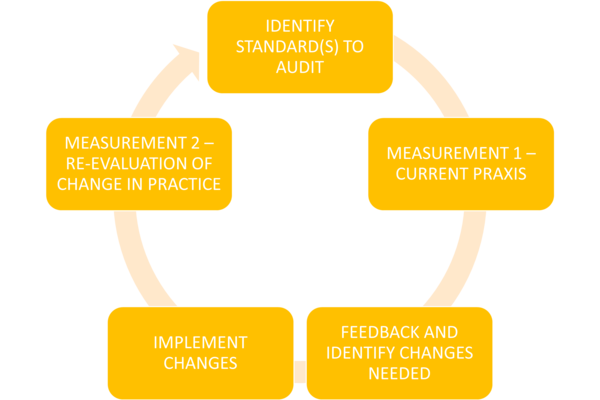
The standard-based audit cycle
To support Quality Improvement, the Takeda/Global Fund programme in 5 countries (Chad, Kenya, Nigeria, Tanzania and Togo) focuses on standards-based (clinical) audit1, which is the systematic review of the quality of care compared to standards of care agreed by all the relevant health managers and providers. The process of standards-based audit follows five steps, known as the 'audit cycle':
- Identify a standard(s) for audit
- Assess current practice and compare against agreed standard(s)
- Where standard(s) are not met, a root cause analysis (why) is conducted to understand the reasons for this and used to identify which changes (remedial actions) are needed
- Actions are implemented
- Practice is re-evaluated subsequently (e.g. 3-4 months interval).
1 Graham W, Wagaarachchi P, Penney G, McCaw-Binns A, Antwi KY and Hall MW. Criteria for clinical audit of the quality of hospital-based obstetric care in developing countries. Bull WHO 2000, 78(S): 614-20
The Quality Improvement interventions utilise materials developed by LSTM, including published manuals for improving the quality of Antenatal (ANC) and Postnatal (PNC) care. The manuals outline the essential steps needed to conduct standards-based audit and set out internationally agreed standards including for women- and baby-friendly care, organisation of ANC, management of obstetric complications, PNC for both mother and baby and management and/or prevention of malaria, TB, HIV and other infections.
Each standard has a clearly stated and measurable objective as well as criteria for what resources will be required to achieve the standards (structure), what actions will be needed (process) and the expected results (outcomes). We have developed a manual that describes, in a simple manner, a step-by-step approach to Standards-based Audit. The manual should facilitate the introduction or strengthening of standards-based audits at the health care facility level, as a method for improving the quality of antenatal and postnatal care, and supports an integrated approach to the delivery of HIV/AIDS, Malaria and Tuberculosis services during and after pregnancy and childbirth.
The manual is meant for use by healthcare providers working in low- and middle-income countries in sometimes very difficult situations, striving to provide good quality of care. The manual is both in English and French versions.

There are currently two interventions under the QI theme:
National review of standards for antenatal and postnatal care
This one day workshop is a platform for key stakeholders to identify, review and agree on a list of standards to be used as markers of quality of care for antenatal and postnatal care, with indicators that can be deployed at healthcare facility level to measure quality of care offered. The discussion is facilitated by LSTM and in-country programme leads using a standardised format validated in several countries.

Standards-based audit introduction and follow-up
This package aims to strengthen a culture of quality improvement in ANC and PNC while integrating three diseases (HIV, TB and Malaria) and building capacity for standard-based (clinical) audit in ANC and PNC. As part of the initial workshop, there is formation of quality improvement teams and planning for standard based audit at a facility. The contents, in addition to providing an introduction and tools for deploying standard -based audits in healthcare facilities, incorporates data-for-decision making training to strengthen capacity for data collection and use as part of the audit.
Methods
To make the course accessible to as many health providers as possible and to be cost-effective, the existing QI course was modified to use a blended learning approach. This comprised Self-directed learning (SDL) using the World Continuing Education Allicance (WCEA) online platform, online group learning (zoom sessions), and face-to-face (F2F) group learning. Material from the previous synchronous QI course were used as a foundation for the new blended learning course. Using an Excel matrix, each content was allocated to the pedagogic approach most appropriate, ensuring adequate coverage and avoiding unnecessary duplication. The course presentations and support materials were developed, reviewed and recorded by members of the team. A participant workbook containing templates and worked examples and a detailed facilitators’ manual were developed.

More information:
- Blog 21 APR 2023: Innovation in learning to improve quality of care in maternal and newborn health
- Launch on WCEA platform - narrative: Quality of care (QoC) Improvement (QI) Blended Learning Course